
This approach enables the removal of significant amounts of CO2 from cement, but also lime, and paper production, by eliminating the need for fossil fuels, with the full electrification of the thermal process and the production of a cleaner process gas, not contaminated by combustion products.
Our modern society is dependent on many materials produced through high temperature industrial processes associated with large CO2-emissions. As we will still require these products in the future, there are several initiatives ongoing in moving these processes away from fossil fuels. ELECTRA is one such initiative, focusing on limestone, paper pulp, and cement.
These materials have one thing in common in that in addition to requiring energy demanding high temperature processing, their production is associated with calcination of calcium carbonate CaCO3, a chemical compound found in limestone and chalk. The calcination itself is an intermediate temperature process (around 900 °C) where calcium carbonate (CaCO3) transforms into calcium oxide (CaO) through the release of chemically bound CO2.
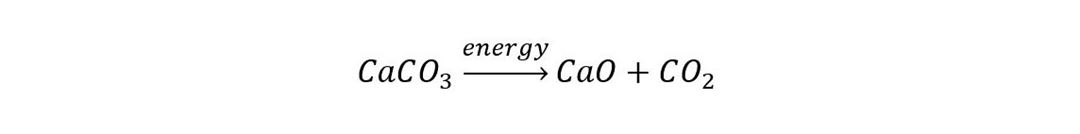
Conversion to calcium oxide is essential to these processes, the electrification of the heating process will not eliminate these process related CO2-emissions. However, as opposed to combustion-heated processes, the CO2 will not be blended by other combustion products. A high purity CO2-stream can be generated by the electrified process, simplifying the carbon capture and storage (CCS). In addition, electrification will obviously eliminate the CO2-emissions connected to combustion.
This process (calcination) can be electrified by resistive heating elements, or by utilizing the process heat from the kiln or a combination of both.
Cement-production requires not only calcination, but also the clinkering process at even higher temperatures, making it the most demanding.
During clinkering, the CaO undergoes several reactions, the most important of these are the reactions with SiO2 into calcium silicates:

These reactions require elevated temperatures (>1300 °C) not achievable by resistive heating technologies. Alternative solutions are therefore required, which are capable of industrial scaling, providing power ratings in the MW to GW range, and are robust in implementation. Thermal plasma torches can tick all these boxes. In addition, they can operate with CO2 as the plasma gas, which means that the released CO2 from the calcination will not be diluted with any other gases.
ELECTRA targets the electrification of both calcination and clinkering processes by investigating alternative heat sources for rotating kiln applications, fluidized bed reactors and electrical heated gas streams.
SINTEF's contribution is the development and adaptation of our in-house designed plasma torch technology, where a patent application has been submitted in late 2024. This plasma torch is unique and especially suited for the required environment, temperature and industrial complexity. Nevertheless, these torches are new to this environment and require testing and validation. For this purpose, SINTEF has designed and built a dedicated plasma torch testing reactor which will give unprecedented opportunities for in situ observation of plasma arcs. The plasma torch development goes together with the modifications and adjustments to the industrial reactors / kilns where the torches are to be implemented. SINTEF is also building and piloting a pilot scale rotating kiln where our plasma torch will be used for calcination and clinkering of up to 500 kg of raw materials per hour.
SINTEF will also contribute to the techno-socio-economic and life-cycle analyses of electrified cement, lime and pulp industry. The applicability of the ELECTRA technologies will be validated through evidence-based analysis of economic, environmental, and societal impacts, where the system design review and techno-economic analyses are led by SINTEF.

